- Osteoarthritis, a common form of joint deterioration, stems from the wearing down of protective cartilage over time.
- Age, excess weight, previous joint injuries, and genetics are significant risk factors for developing osteoarthritis.
- Certain treatments, like platelet-rich plasma, have shown promise in managing osteoarthritis symptoms and slowing disease progression.
- Regular low-impact exercises, maintaining a healthy weight, and protecting joints during activities can help prevent osteoarthritis.
- Even with genetic predisposition, active measures can reduce osteoarthritis risk; consult a healthcare provider for symptoms.
One common form of joint deterioration is osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis affects millions worldwide and can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling in the affected joints. While some people are more susceptible to developing osteoarthritis due to genetic factors, there are also many ways in which we can increase our risk of developing this condition. Here’s a look into the disease, ways you’re susceptible to it, and ways you can prevent it.
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis, or degenerative joint disease, is arthritis that occurs when the protective cartilage in your joints wears down over time. This can happen due to age, injury, or repetitive joint stress. As the cartilage breaks down, bone-on-bone contact occurs, leading to pain, stiffness, and inflammation in the affected joint. Osteoarthritis mostly affects joints that carry the weight of the body.
Risk Factors for Osteoarthritis
While age is a common risk factor for osteoarthritis, there are several risk factors for the disease. Here are some of them:
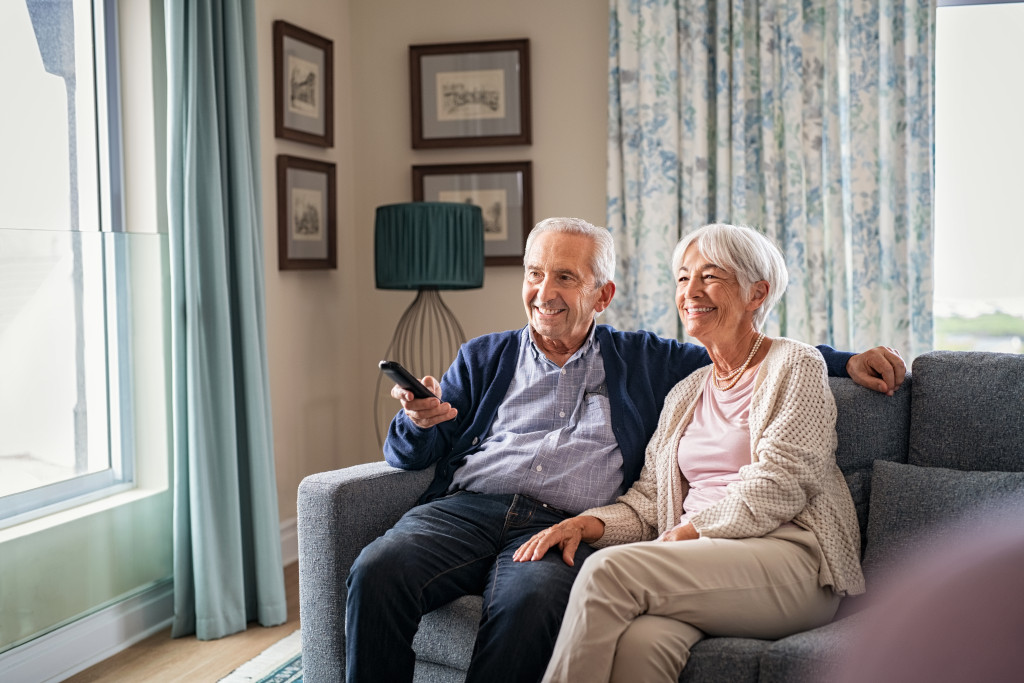

1. Aging
The cartilage quality that cushions the joints deteriorates, making it more susceptible to damage as people grow older. This is why osteoarthritis is more common in older individuals. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), one in two adults over 65 experience arthritis symptoms.
2. Excessive Weight
Carrying excess body weight can put a significant amount of pressure on your joints, leading to the gradual degeneration of cartilage. According to the Arthritis Foundation, each weight gain puts four pounds of pressure on the knee joints. This can eventually cause the joint to wear down and increase your risk of osteoarthritis.
3. Previous Joint Injuries
If you’ve had a joint injury, it can increase your likelihood of developing osteoarthritis in that joint. The injury may have damaged the cartilage or bone surfaces, making them more susceptible to wear and tear. This is especially true for athletes or individuals who participate in high-impact activities regularly.
4. Genetics
While not entirely preventable, genetics can affect your susceptibility to osteoarthritis. Researchers have identified several genes that can increase an individual’s risk of developing the condition. Suppose you have a family history of osteoarthritis. In that case, it’s essential to take steps to minimize your risk by maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and seeking treatment for any joint injuries.
Ways to Prevent Osteoarthritis
While you cannot control all risk factors for developing osteoarthritis, there are steps you can take to prevent the disease or manage its symptoms. Here are some ways to do so:
PRP Treatment
There are specific treatments that are better at dealing with the disease than others. A platelet-rich plasma treatment utilizes the body’s natural healing process to repair and regenerate damaged tissues, including cartilage in joints affected by osteoarthritis. This treatment has shown promising results in managing symptoms and slowing down the progression of the disease.
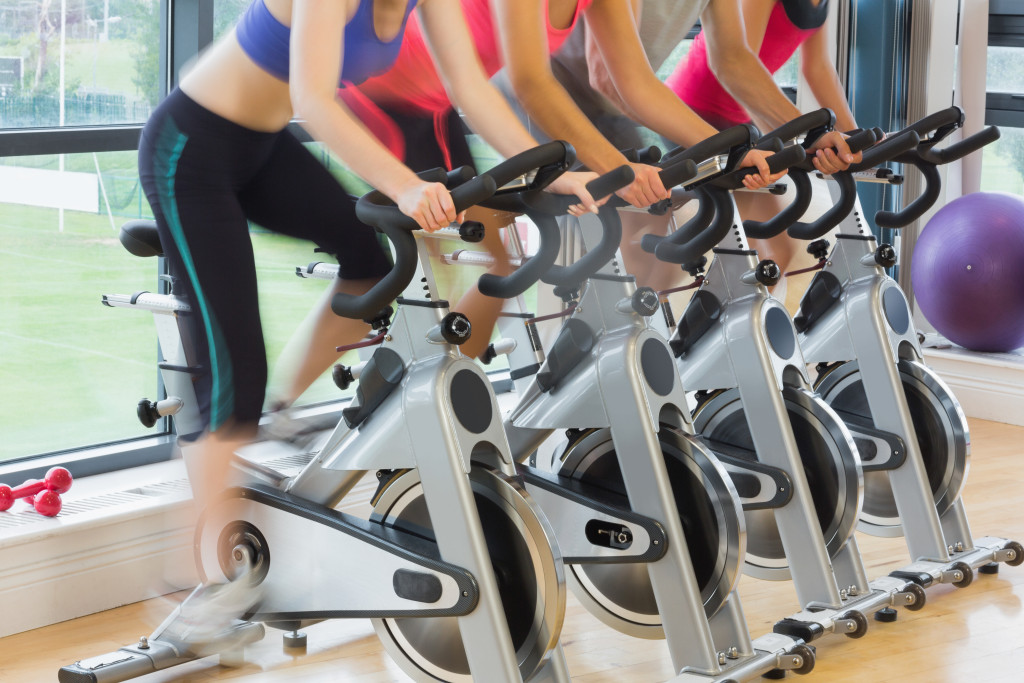

Exercise Regularly
Regular physical exercise can help keep your muscles strong and maintain healthy joints. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, or yoga can help improve joint flexibility and reduce pain caused by osteoarthritis. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise routine.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
As mentioned earlier, excess weight can strain your joints, leading to the breakdown of cartilage. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet can help prevent or manage osteoarthritis. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can also provide the necessary nutrients for joint health.
Protect Your Joints
If you participate in activities that put stress on your joints, it’s essential to take precautions to prevent injury. This includes wearing protective gear, using proper technique and form during exercise or sports, and taking breaks when needed.
Osteoarthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While some factors, like genetics, are outside of people’s control, there are several ways you can minimize your risk of developing osteoarthritis. By maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and treating joint injuries promptly, you can protect your joints and reduce your susceptibility to this condition. If you’re experiencing any joint pain or stiffness, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to get an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.